Adobe Photoshop Color settings in digital imaging demands the precise settings to ensure your artwork remains constant whenever used through multiple media and devices. In Adobe Photoshop, an integrated set of color settings helps a user manage the color in such a manner that the result remains the same at every step of their creative workflow.
Table of Contents
Understanding in Adobe Photoshop Color Settings
Photoshop Color Settings is ensuring that the various color representations held by different devices–monitors, printers, and cameras and so on-all agree on giving the same outcome in color presentation. Photoshop colors are interpreted via color profiles which will guarantee your monitor displays images exactly as if they will finally appear in their output.
Steps to Accessing Photoshop Color Settings
To activate or set up Photoshop color settings :
- Open Photoshop application.
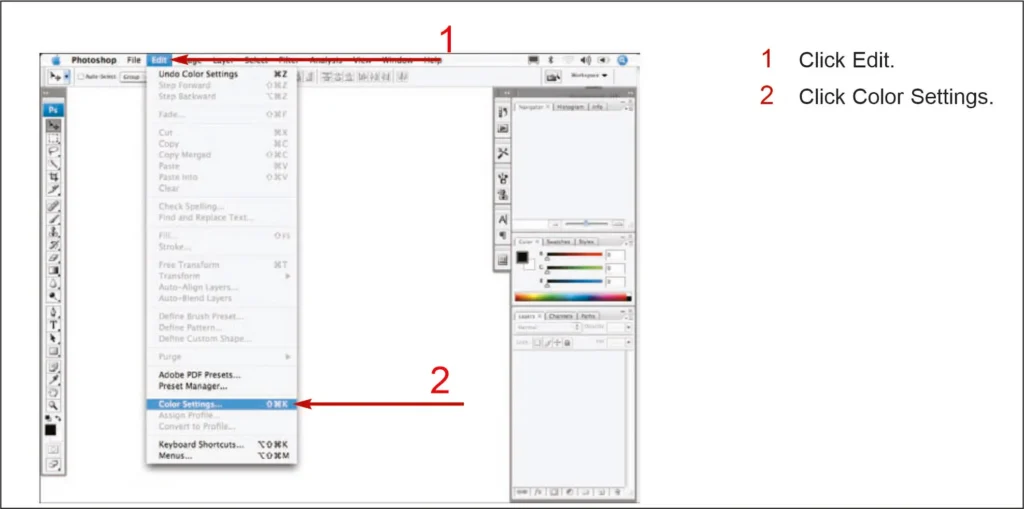
- Open the “Edit Menu” :
- Click Edit on the top menu bar.
- From the drop-down, click on Color Settings.
This opens the Color Settings dialog box from which you can set several parameters to your workflow.
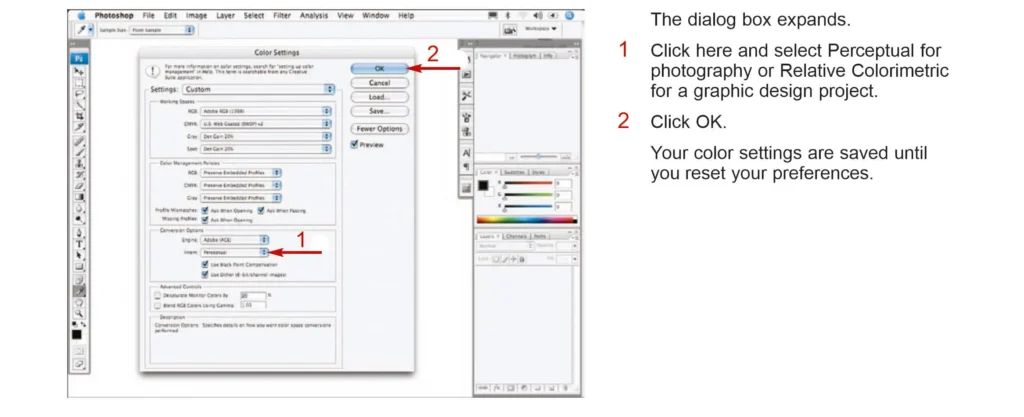
Setting Working Spaces
Working spaces define the color profiles that Photoshop uses for editing images. It is very important to set up appropriate working spaces to maintain color accuracy.
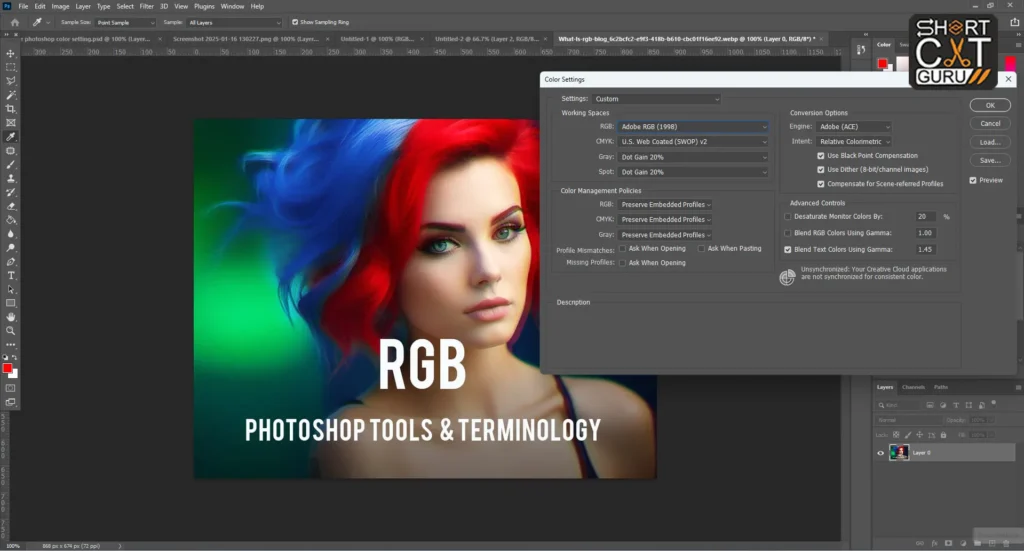
RGB Adobe Photoshop color settings
The RGB working area defines how colour is represented within your monitor. Photoshop offers numerous RGB color profiles, each in a different color gamut as follows:
- sRGB IEC61966-2.1, best suited to web graphics, and online pictures because of color gamut range.
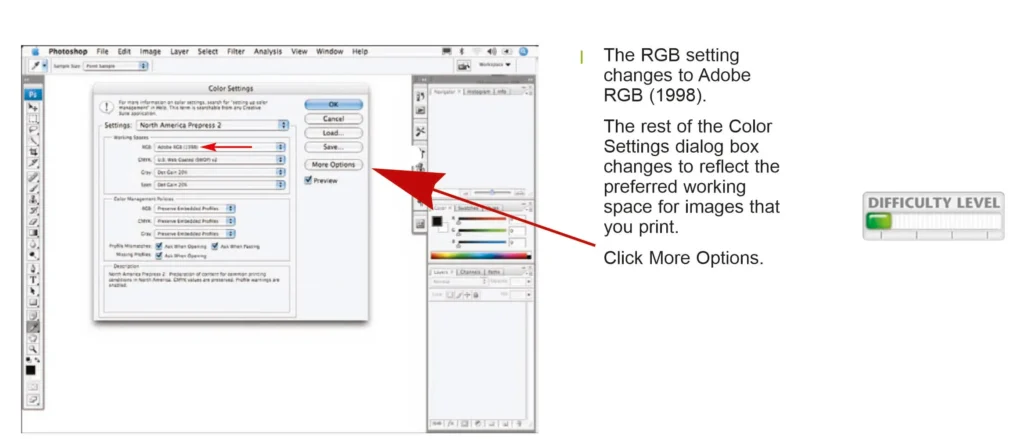
- Adobe RGB (1998), best applied to print workflows since it produces a wider colour gamut that sRGB provides.
- ProPhoto RGB: Wide color gamut. It would be used in very high-end imaging. It requires extreme care so that no color issue happens.
Recommendation: For most users, setting the RGB working space to Adobe RGB (1998) balances a wide color gamut with manageable file sizes, making it suitable for both print and digital media.
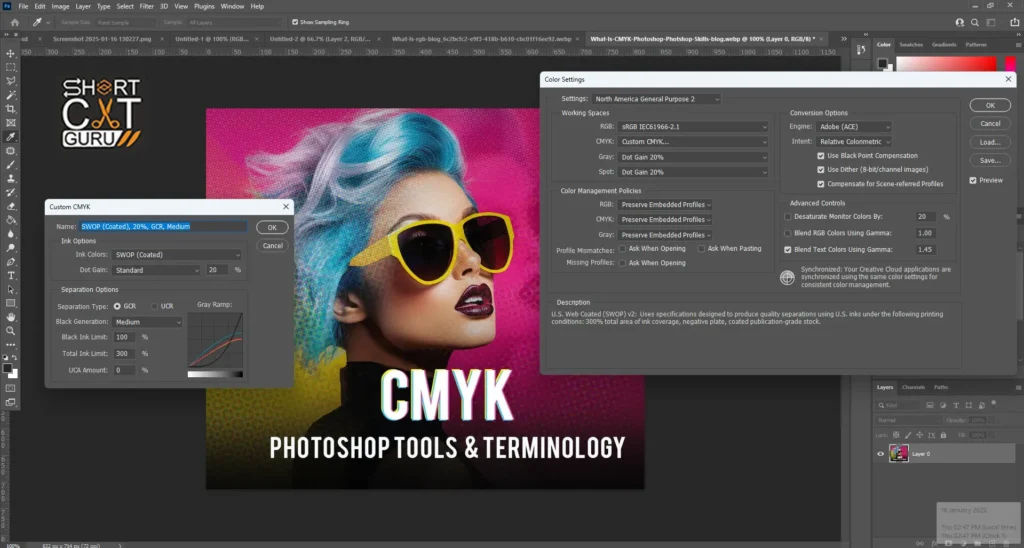
CMYK Adobe Photoshop color settings
The CMYK working space refers to how the colors are separated for printing purposes, which is essential in the print production line. Choosing a suitable CMYK profile ensures the printed colors coincide with your on-screen design.
Choose a CMYK profile that is within the ability of your printer or the desired standard of your print service provider. Some profiles include:
- U.S. Web Coated (SWOP) v2: This is the standard U.S. web offset printing
- Coated FOGRA39 (ISO 12647-2:2004): The European printing standard
Gray and Spot Working Spaces
These profiles regulate the appearance of grayscale and spot colors.
- Gray: For grayscale images, the Gray Gamma 2.2 is usually applied.
- Spot: These are for the spot color channels of printing. Choose profiles according to your requirements.
Color Management Policies
The policies of Photoshop decide how it manages color profiles while opening and saving files.
RGB, CMYK, and Gray: Adobe Photoshop color settings
- Preserve Embedded Profiles: This maintains the color profiles of images imported to ensure consistency.
- Convert to Working RGB/CMYK/Gray: Converts images to the working space currently, which is very helpful for standardizing files but might change appearance.
- Off: Disregards embedded profiles, which may cause color inconsistencies and is not recommended in general.
Recommendation: Preserve Embedded Profiles for Setting Policies to Make sure the working color is consistently maintained while operating on files derived from other origins.
Handling Profile Mismatches and Missing Profiles
Photoshop may open some files containing missing or mismatching color profiles of images.
Profile Mismatches:
- Ask When Opening: Instructs Photoshop to make you decide which profile to apply, convert the embedded profile to a working space or discard it altogether.
- Ask When Pasting: This alerts you every time you paste content that has a different profile so you can deal with color consistency.
Missing Profiles:
- Ask When Opening: It lets you know whether an image doesn’t have an embedded profile and lets you set the correct working space.
Recommendation: Let these options be allowed so that you keep in control the decision of color management in your workflow.
Advanced Controls Adobe Photoshop Color Settings
For users requiring fine-grained control over color management, Photoshop offers the following advanced settings:
Conversion Options:
- Engine: The Adobe (ACE) engine is the default and recommended color conversion engine.
- Intent: Determines how colors are converted between profiles. There are a variety of intents. The most common intents include:
- Perceptual: The visual relationship between colors is preserved, best suited for images intended for photorealistic renderings.
- Relative Colorimetric: In-gamut colors are preserved exactly; out-of-gamut colors are clipped; best used for preserving the color exactly.
Apply Black Point Compensation:
This ensures that the shadow details are preserved in the color conversion.
Apply Dither (8-bit/channel images):
Dithering is applied to minimize banding in gradients during color conversion.
Recommendation: Unless you have special requirements, the default advanced settings are usually good enough for most workflows.
Saving and Loading Adobe Photoshop Color Settings
Photoshop allows you to save custom color settings for consistency in projects and teams.
Save:
- Once you have set your preferences, you would click the Save button of the Color Settings dialog box.
- Type in a descriptive name and save the .csf (Color Settings File) for future use.
Load:
- To load saved settings, click the Load button of the Color Settings dialog box.
- Browse for the .csp file and select it to apply your defined color settings.
Tip: Keeping a library of .csf files for various workflows, such as print, web, or multimedia projects, ensures consistent results and saves time when switching between projects.
________________________________________
Best Practices for Adobe Photoshop Color Settings
To get the best possible results in your projects, here are some best practices:
Calibrate and Profile Your Monitor
Why It Matters: Monitors display colors differently, and calibration ensures accurate color representation.
How to Calibrate:
- Use hardware calibration tools like a colorimeter.
- Software options like Adobe Gamma or DisplayCAL can be used to calibrate.
- Set your monitor’s color temperature to 6500K and gamma to 2.2 to view your work in standard viewing conditions.
Match Color Settings Across Software
Synchronize color settings among Adobe applications using Adobe Bridge:
- Open Adobe Bridge.
- Go to Edit > Color Settings.
- Choose a preset or manually sync settings with Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign.
Work in a Neutral Environment
- Make sure your workspace is free from strong lighting or color casts that may affect perception.
- Use neutral gray backgrounds on your monitor and workspace to avoid color bias.
Preserve Source Profiles
- Always save images with embedded profiles to retain the original color data.
- When working in collaboration, communicate the profiles and settings used to ensure consistency.
Test and Proof Your Workflow
- Soft Proofing: Use Photoshop’s Proof Setup feature to simulate the final output on your monitor.
- Hard Proofing: Print test copies to evaluate colors before mass production.
Maintain Industry Standards
- Keep your software and color profiles updated in compliance with the most recent color management standards.
________________________________________
Frequent Problems and Solutions with Color Management
Colors Appear Differently on Screen and Print
- Reason: Conflicting color profiles or uncalibrated devices.
- Solution: Set up working space and printer profiles correctly. Calibrate your monitor for a good screen-to-print match.
Profile Mismatch Warnings
- Cause: Files have profiles that are not your working space.
- Solution: Turn on Ask When Opening in color management policies so these kinds of situations can be addressed in a case-by-case fashion.
Images Look Washed Out or Over-Saturated
- Cause: Working in the wrong color space.
- Solution: Web Use: sRGB. Print – files must be in Adobe RGB (1998) or a CMYK profile by the printer used.
________________________________________
Troubleshooting Advanced Color Issues
Although the color management tools in Photoshop are pretty strong, some problems may demand more in-depth knowledge for expert users. Here are a few advanced troubleshooting tips:
Banding in Gradients
- Cause: Lack of adequate color depth or wrong dithering settings.
- Solution:
- Work in a 16-bit or 32-bit color depth to minimize banding.
- Turn On Dither in the Color Settings dialog for 8-bit images.
- Add noise to the gradient as a quick fix to lay over banding in extreme situations.
Color Shift After Exporting Files
- Cause: Color space mismatch at export.
- Solution:
- Ensure that the export settings match the destination-web or print.
- For web, convert the image to sRGB before saving to ensure it will display consistently on all devices.
- For print, save the file in a CMYK profile that matches the printer’s requirements.
Blacks Print Washed Out
- Cause: Black point compensation is not set correctly or the profile is not correct.
- Solution:
- Check that Use Black Point Compensation is enabled in the Color Settings.
- Confirm that the selected CMYK profile matches your printer’s specifications.
- Consider creating a custom CMYK profile for high-precision printing workflows.
________________________________________
Advanced Workflow Tips for Professionals
Using Proof Colors for Accurate Output Simulation
Simulate how your work will look on various devices or in print with Photoshop’s Proof Colors feature
- In View > Proof Setup choose a preset: Working CMYK or one you’ve made with a different profile
- In View > Proof Colors activate the simulation preview
- Adjust colors while simulating output proofing in real-time
Pro Tip: In View > Gamut Warning view the colors out of gamut
Actions: Streamline Repetitive Tasks
Photoshop Actions are ideal for streamlining workflow when repeating similar tasks
- Open the Actions Panel, Window > Actions
- Create a new action and record steps such as assigning color profiles, converting spaces, or applying adjustments.
- Save the action and apply it to batch processes for efficiency.
Third Party Tools and Plug-Ins
Third party tools fill in the gaps to address complex demands that Photoshop’s colour management cannot handle;
- ColorThink Pro : Analyzing and visualizing profiles for further analysis
- i1Profiler by X-Rite : Calibration and profiling for a device with perfect accuracy.
- SoftProof by Chromix : Colour conversion process to simplify and save time from unnecessary softproofing
_____________________________________
Resource for Further Research
To develop knowledge on the subject, find further information about:
Adobe Official Documentation: Adobe Color Settings
Books: Adobe Photoshop color settings
- Real World Color Management by Bruce Fraser and Chris Murphy
- Color Management for Photographers by Andrew Rodney
Online Tutorials and Courses:
- Adobe Photoshop YouTube Channel
- LinkedIn Learning Photoshop Essentials
- CreativeLive’s Advanced Photoshop Workshops
Staying Current with Industry Developments
The field of digital imaging is constantly evolving, so staying current is key. Get ahead by joining professional organizations, such as the Adobe Photoshop Forums, attending industry shows, like SIGGRAPH, and receiving newsletters from organizations like ICC – International Color Consortium.
________________________________________
Color Profiles: Adobe Photoshop color settings
Color profiles are a foundation to represent colors accurately. Understanding the technical details gives one the ability to have precise control over color rendering.
ICC Profiles and Their Function
What are ICC Profiles?
ICC (International Color Consortium) profiles define the characteristics of devices and allow for reliable color reproduction. Each profile is made up of:
- Device Profiles: These profiles are hardware-specific, such as monitors, cameras, and printers.
- Working Profiles: These detail the default color space for image editing and processing.
How to Enhance the Usage of ICC Profile
- Update your devices’ ICC profiles regularly to ensure that they meet the latest industry standard.
- Use device-specific ICC profiles, like printer profiles, to fine-tune color fidelity even further.
Wide Gamut and Standard Profiles
Wide Gamut Profile
- Pro Photo RGB and Adobe RGB (1998) profiles can capture a bigger color space. This will provide little use to high-end photographers for detailed print work and graphics.
Standard Profile
- sRGB is meant for good images on digital screen and web, thanks to consistent rendering on every device but compresses the gamut.
Pro Tip: Edit in a wide gamut profile and then convert to the appropriate output profile just before export for maximum color detail.
________________________________________
Advanced Output Options
Output settings at finalization allow for tailoring that ensures color accuracy in the target medium.
Soft Proofing for Complex Outputs
For complex workflows, such as high-end printing or digital display installations:
- Use Custom Proof Setup to mimic the precise color output for a particular device or paper type.
- Adjust rendering intents, such as Relative Colorimetric or Perceptual, to understand how colors are interpreted in the final medium.
- Save these settings for reuse on similar projects.
Spot Adobe Photoshop color settings in Professional Printing
Spot colors, used often in branding, demand accuracy to ensure consistency:
- Utilize the Pantone Color Library in Photoshop for industry-standard spot colors.
- Carefully convert spot colors to CMYK so that the final print still retains their color vibrancy and accuracy.
Export Settings for Different Mediums
Web and Screens
- Convert to sRGB.
- PNG or JPEG formats for highest quality and compatibility.
- Export in TIFF or PDF with a CMYK color profile.
- Use embedded profiles so that the output is color accurate.
Video
- Rec.709 is the color space used in most video production.
- Align your export format to the standards of your video editing software.
______________________________________
Synchronization of Teams
When working on a team-based project, teams must be highly standardized in color so that they can have consistency about it.
Sharing Adobe Photoshop color settings
Photoshop’s feature of saving and sharing color settings streamlines the teamwork processes:
- Save your customized color settings as a .csf file
- Distribute this file to other team members to ensure everyone applies the same settings.
Tip: Store settings files in a central folder or in cloud storage, so they can be easily located and updated.
Style Guides
For agencies and teams working on brand-critical projects:
- Develop detailed style guides that include color profiles, gamuts, and output specifications
- Include visual examples of approved color usage and print proofs for reference
_____________________________________
New Horizons in Color Management
Innovations like AI-driven tools and HDR workflows promise to change the future of color management.
AI-Powered Tools
Leverage AI capabilities in Photoshop for tasks such as:
- Auto Color Correction: Machine learning analyzes and balances colors.
- Content-Aware Adjustments: Colors blend together seamlessly in composites.
High Dynamic Range (HDR) Color Spaces
HDR provides a much wider color range and higher brightness levels for today’s displays:
- Edit in HDR10 or Dolby Vision color spaces for projects that will be played back on HDR-capable devices.
- Make sure your monitor is HDR-capable to edit accurately.
________________________________________
Conclusion
It is a very important ability in mastering Adobe Photoshop color settings in order to ensure consistency and quality of your work from each creative project. And it is by configuring your working spaces, knowing color management policies, and following best practices in order to get precise color control from start to finish. Use these techniques in the workflow to upgrade your quality in design and production.
Refer to the official Adobe documentation for more advanced tutorials, industry-standard profiles, or troubleshooting and find new features in Photoshop.
Adobe Photoshop Color Settings – FAQs
1. What is color settings in adobe photoshop
In other words, the word Adobe Photoshop color settings describes what colors are treated, displayed, and saved so that they view correctly on your monitor, scanner, or any other device; it also explains things like color profile, working space, and so on, hence color conversion.
2. How do I obtain access to my Adobe Photoshop color settings?
Now head to the menu bar, select Edit> Color Settings. Then you should open the dialog box Color Settings, from where you can set changes in lots of options.
3. What are working spaces in Photoshop?
In Adobe Photoshop, Color Settings provide color profiles of the working space, describing what is known as the color gamut or color range for any particular job; these profiles for RGB are typically: for any screens digital sRGB, Adobe RGB, and ProPhoto RGB.
- CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black): For print projects.
- Gray: Describes the work space for grayscale.
- Spot: For colours to be used as spot colours in print.
4. What are the variations between sRGB, Adobe RGB, and ProPhoto RGB?
Adobe Photoshop Color Settings gives you a choice from among the various RGB profiles:
- sRGB: Most commonly used for the web and other digital displays, has a fairly small colour gamut.
- Adobe RGB: The gamut is much wider than sRGB. It is ideal for printing and professional photography.
- ProPhoto RGB: Extremely huge gamut. Ideal for detailed retouching and output quality.
5. What are color management policies in Photoshop?
Color management policies in Adobe Photoshop Color Settings defines how the color profiles should be handled by Photoshop. There are
- Preserve Embedded Profiles: The image profile as it is kept.
- Change To Working Space: The colors of the image are translated into the working space.
- Off: Do not take into consideration color management; this may yield unsatisfactory colors.
6. Should I use “Advanced Mode” in color settings?
Advanced Mode within Adobe Photoshop Color Settings provides control over color management at a granular level. It is ideal for professionals, who require more control over rendering intents, black point compensation, and profile mismatches.
7. What are rendering intents, and which should I use?
Rendering intents in Adobe Photoshop Color Settings define how colors are converted between different color spaces:
- Perceptual: Colors are adjusted to maintain overall visual balance. Best for photos.
- Relative Colorimetric: Maintains accurate colors in the target gamut; suitable for most purposes.
- Saturation: Vivid colors are prioritized; used for graphics.
- Absolute Colorimetric: Colors are matched exactly, often for proofing.
8. What are ICC profiles for in Photoshop?
ICC Profiles are an important part of the Adobe Photoshop Color Settings that specify how to translate the colour created on devices so that the appropriate colours can be represented on many monitors and the majority of output devices.
9. How would I handle a mismatch profile?
When you want to open the image to which you’ve applied a colour profile other than your active working space. You may always open up the options using ‘Use Embedded Profile’. This above option has it as in its original creating.
- Convert to Working Space : Assign the file with your current color settings.
- Apply Embedded Profile: Apply a profile and Use embedded profile setting.
10. What are defaults Color Settings of Photoshop?
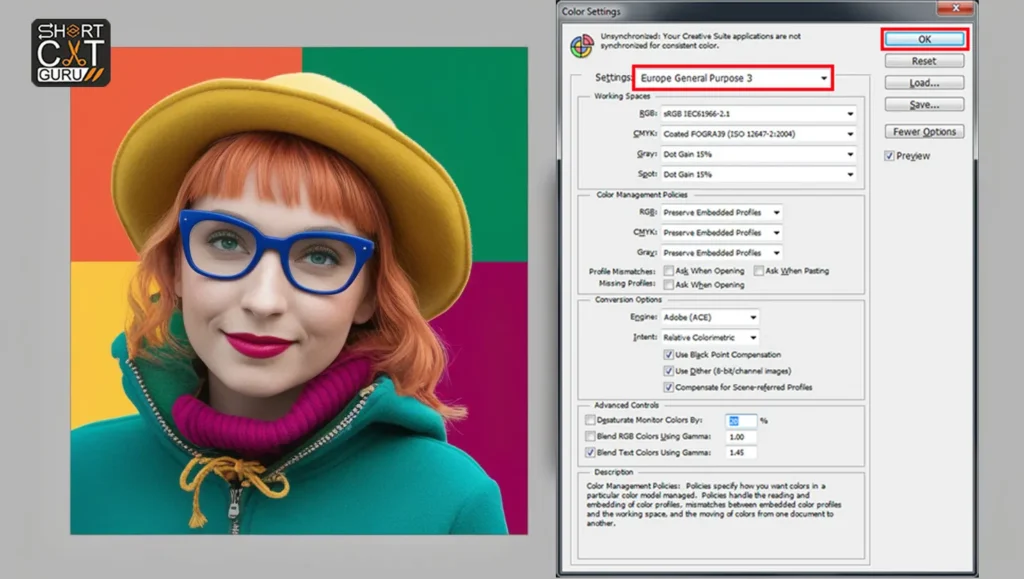
Default Adobe Photoshop Color Settings varies with region
- North America General Purpose 2: RGB, and U.S. Web Coated (SWOP) v2 for CMYK
- Europe General Purpose 3: RGB, and Coated FOGRA39 for CMYK.
- Japan Color 2001 Coated: It is settings which are best for Japanese print standard.
11. How to synchronise colour settings throughout all Adobe applications?
To synchronize Adobe Photoshop Color Settings between Adobe applications, you can use Adobe Bridge. Press Edit > Color Settings in Bridge; then choose a preset and apply it to all your Adobe Creative Cloud applications.
12. How do I reset color settings to default?
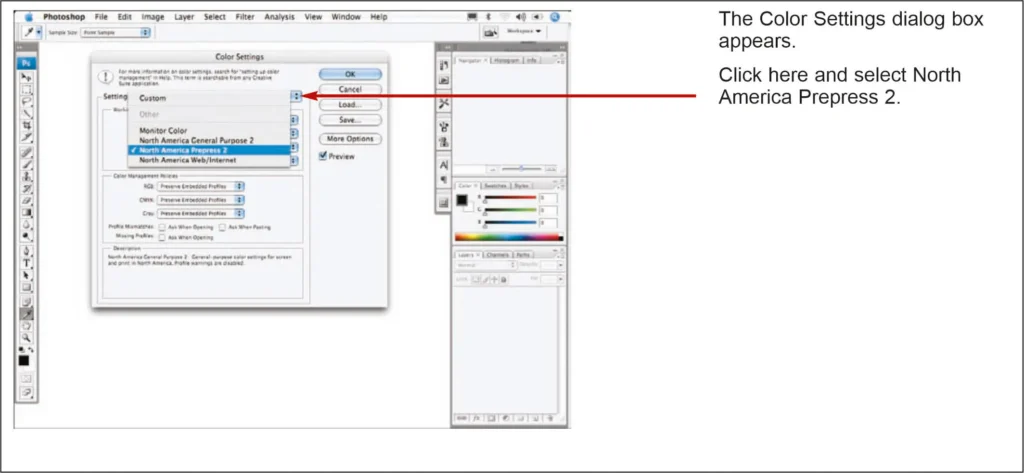
In the Adobe Photoshop Color Settings dialog box, select More Options, then a region-specific preset -for instance, North America General Purpose 2.
13. Why is my color coming out differently on Photoshop than it does on all my other devices?
This might be due to differences in monitor calibration, color profiles, or device-specific color gamuts. Using ICC profiles consistently and making adjustments in the Adobe Photoshop Color Settings will also help improve the color rendering.














Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?